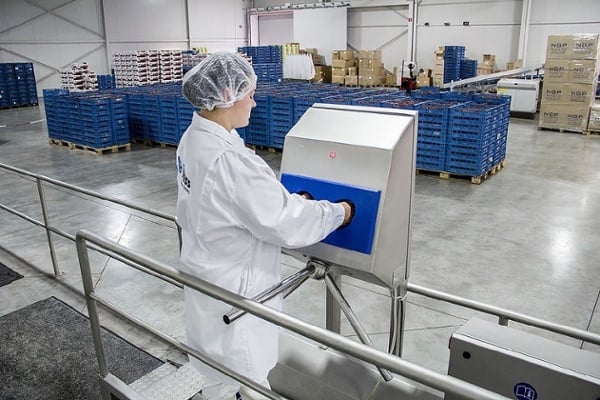
Hygienic Room
Hygienic Room:
Industrial hygiene has been defined as “that science and art devoted to the anticipation,recognition, evaluation, and control of those environmental factors or stresses arising in or from the workplace, which may cause sickness, impaired health and well-being, or significant discomfort among workers or among the citizens of the community.” Industrial hygienists use environmental monitoring and analytical methods to detect the extent of worker exposure and employ engineering, work practice controls, and other methods to control potential health hazards.
There has been an awareness of industrial hygiene since antiquity. The environment and its relation to worker health was recognized as early as the fourth century BC when Hippocrates noted lead toxicity in the mining industry. In the first century AD, Pliny the Elder, a Roman scholar, perceived health risks to those working with zinc and sulfur. He devised a face mask made from an animal bladder to protect workers from exposure to dust and lead fumes. In the second century AD, the Greek physician, Galen, accurately described the pathology of lead poisoning and also recognized the hazardous exposures of copper miners to acid mists.